Photo: Deutsches Museum | Christian Illing
Communication Information Media
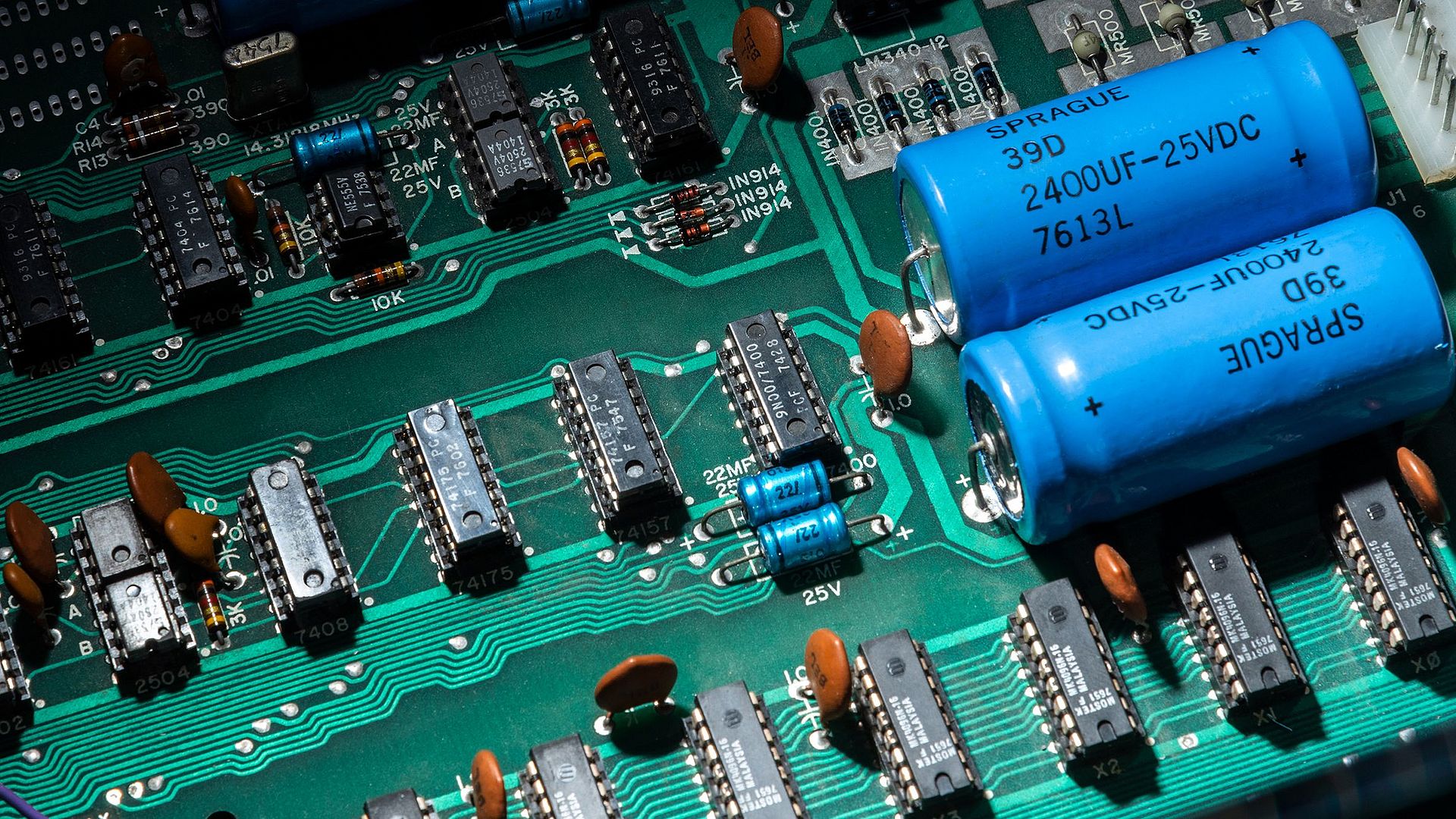
Microelectronics – from Quartz Crystals to the Microchip
Our modern everyday life would be unimaginable without microchips. Immerse yourself in this microscopic world and learn more about the increasingly tiny circuits that have such a lasting impact on our lives.
What is Microelectronics?
Microelectronics has been a topic of discussion ever since it became possible to combine the various functions of electronic components, including diodes, transistors or resistors, on a single semiconductor device. This was first achieved in 1958 – and from 1970 it led to the development of integrated circuits such as microprocessors and memory chips, which combine complex circuits in one single tiny package. The miniaturisation that accompanied microelectronics revolutionised communications and information technology and – from pacemakers and washing machines to robots – it can be found in every technological device. In the modern world, nothing works without microelectronics.
Photo: Deutsches Museum | Christian Illing
- From Electronics to Microelectronics
Transistors represent the transition from electronics (vacuum tubes) to microelectronics (integrated circuits). They utilise the properties of semiconductors such as germanium or silicon. - Diversity of Microchips
Memory chips, microprocessors and microcontrollers are among the most commonly used microchips. Their design differs depending on the required computing speed – either as bipolar or field-effect transistors. - Applications of Microelectronics
Microchips can be found in almost every modern device – from computers and pacemakers to washing machines and industrial robots. Microchips are primarily responsible for controlling and regulating the many functions of these devices. - Microelectronics and Computer Science
The development of microelectronics is closely linked to the development of computer science, especially programme control. Complex systems, for example image recognition, can only be implemented with the help of microelectronic circuits and special software.
Inside the Microelectronics Exhibition
Insights into the History of the Telephone
In our M*Vlog series, Pauline Diebenbusch, junior member of the Freundes- und Förderkreis Deutschen Museums e.V. (Friends and Sponsors of the Deutsches Museum), talks to Luise Allendorf-Höfer, curator of Communications Technology and Electronics, about the history of the telephone. The film is currently only available in German.
Any Questions?
![]()
Dipl.-Ing. Luise Allendorf-Hoefer
Curator
Telecommunications, Microelectronics DepartmentDeutsches Museum
80306 MunichTelephone +49 89 2179 269
Fax +49 892179 99350
Email l.allendorf-hoefer@deutsches-museum.de
Do you have organizational questions?
Cornelia Schubert
Assistance to department heads, main department heads and curators
Susanne Schmölz
Assistance to department heads, main department heads and curators

